Automatically Generate Embeddings with Supabase and Cloudflare Workers
Recently, while working on my project, TurboForm, I needed an efficient way to make form responses searchable using AI (to eventually build a “chat with your data” feature).
In this post, I’ll show you, step by step, how to automatically generate embeddings with Supabase and Cloudflare Workers. If you’re new to the concept of embeddings, feel free to check out this post before proceeding.
To make this process seamless, we’ll follow these steps:
- Enable the required Supabase extensions. This lays the foundation for handling messaging and vector storage in your database.
- Add a vector column to your database table. This column will store the embeddings generated for each row.
- Set up a queue to capture new or updated rows. The queue receives an event for every change that will later be processed by the Cloudflare worker.
- Create a database trigger that queues events for embedding generation. This trigger fires whenever a new row is added or updated.
- Process queue messages using a Cloudflare Worker endpoint. The worker reads the messages and generates embeddings in real-time.
- Schedule a CRON job to trigger the worker periodically. This ensures that embeddings are continuously updated.
Let’s get started!
Enable all necessary extensions in your Supabase database
To accomplish the above steps you will require 4 extensions:
pg_cron- to create CRON jobs in PostgreSQLpg_net- to make HTTP calls from PostgreSQLpgmq- to enable a message queue built on PostgreSQLvector- to enable vector storage in your DB tables
These extensions can be enabled via the Supabase dashboard as shown in the screenshot below (recommended):
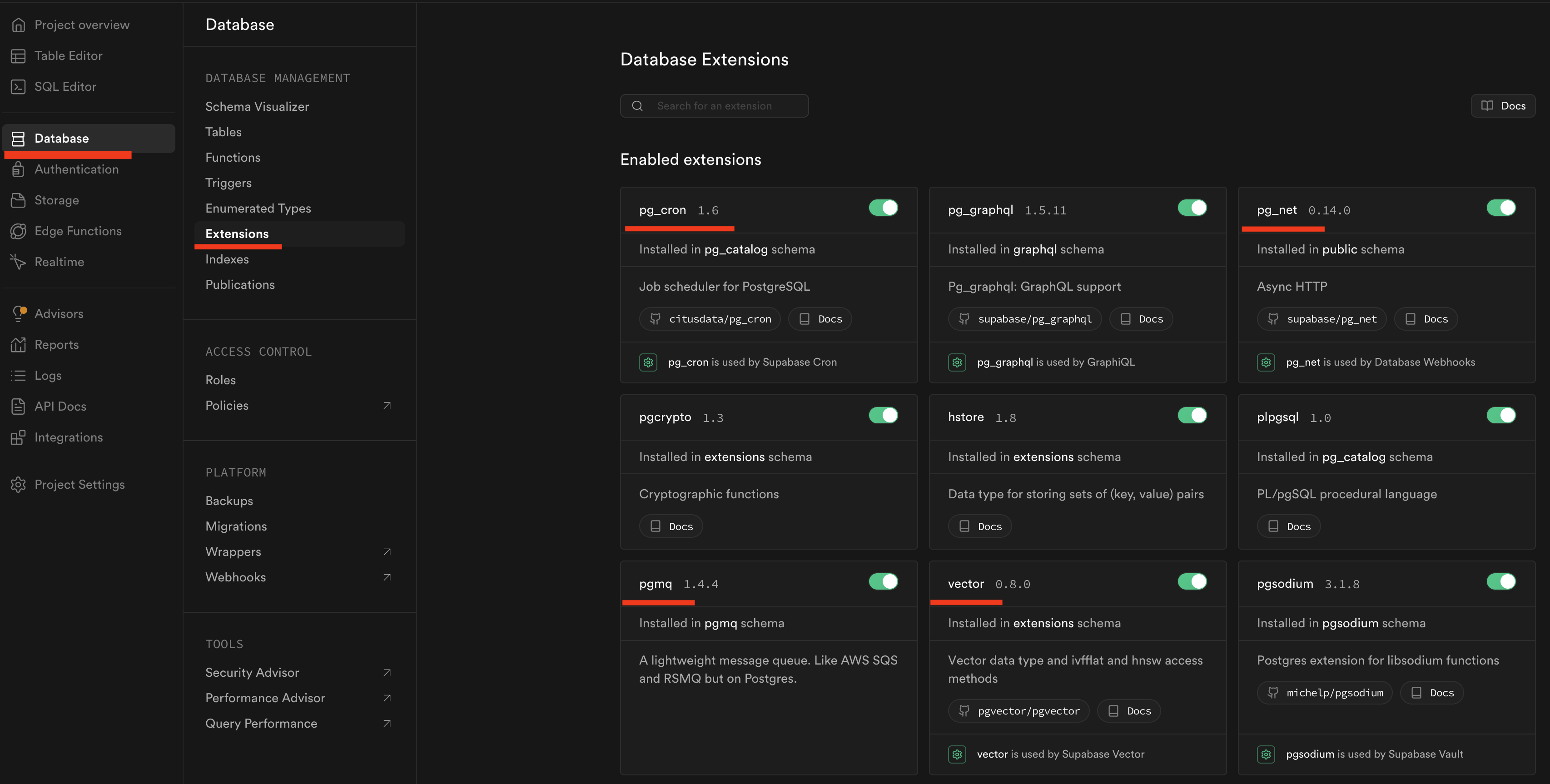
Or by running this SQL script:
create extension if not exists pg_cron;
create extension if not exists pg_net with schema public;
create extension if not exists pgmq;
create extension if not exists vector with schema extensions;Add a vector column to your database table
For the purpose of this post, let’s create a table with this SQL script. The embedding column will store the embeddings generated for each row.
-- Create responses table
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS public.responses (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY DEFAULT uuid_generate_v4(),
answer text NOT NULL,
embedding vector(1536),
created_at TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT NOW()
);
-- Create HNSW index for vector search for better DB performance
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS responses_embedding_idx
ON responses
USING hnsw (embedding vector_cosine_ops)
WITH (m = 16, ef_construction = 64);
Set up a queue to capture new or updated rows
Create the queue directly in the Supabase dashboard as shown in the screenshot:
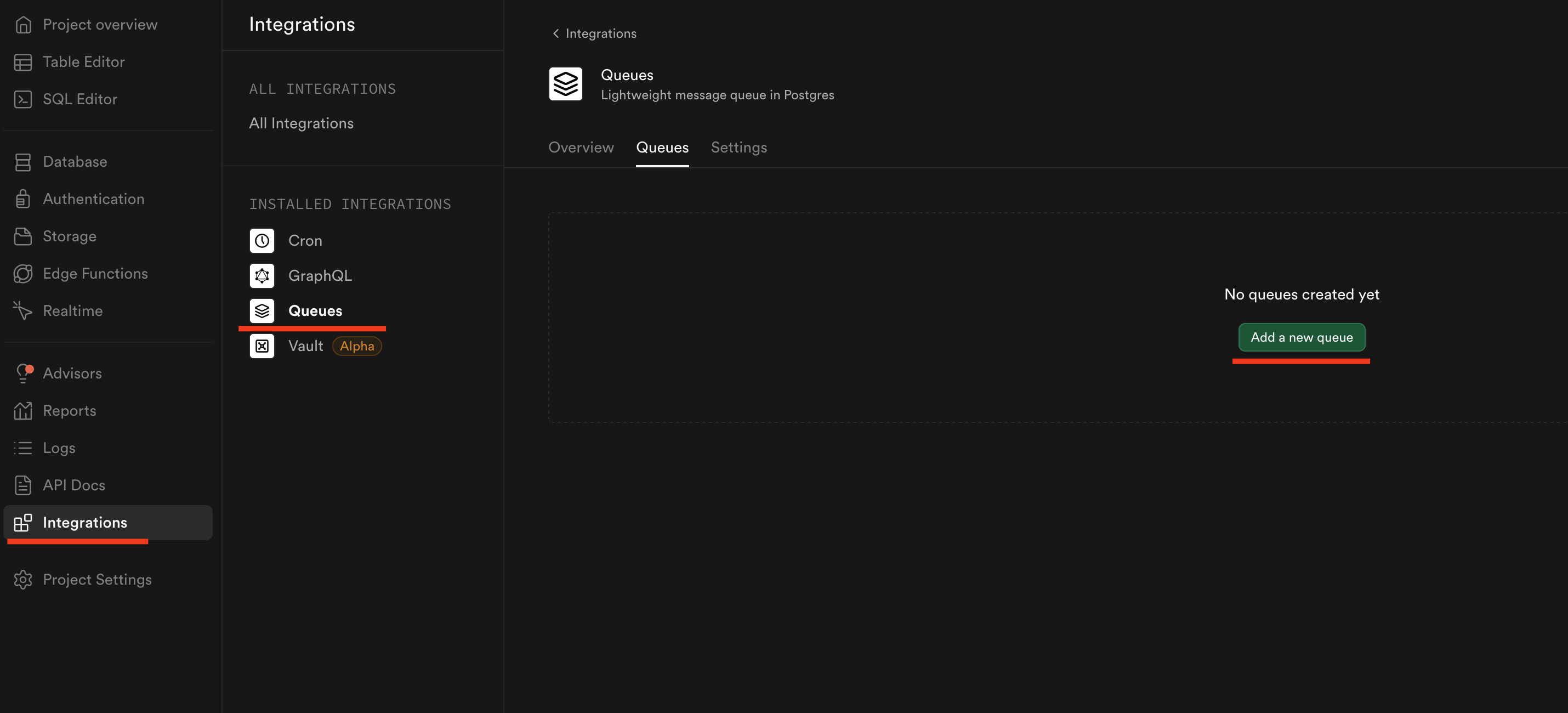
Or run this SQL script:
SELECT pgmq.create('response_embeddings');After creating the queue, make it accessible via the Supabase public API. This is necessary to call the database functions in the pgmq_public schema with remote procedure calls via the Supabase client libraries, e.g. supabase.rpc('').
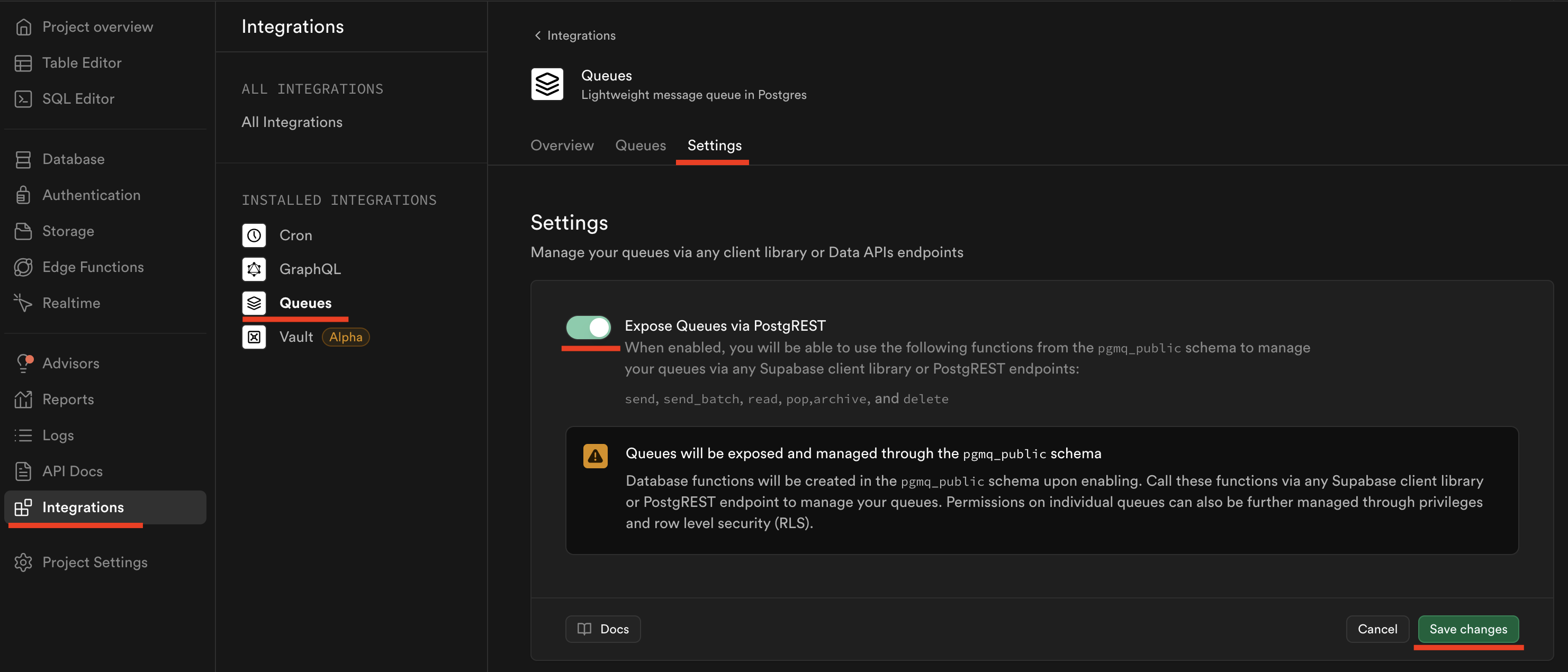
Also, ensure that the pgmq_public schema is exposed via the data API.
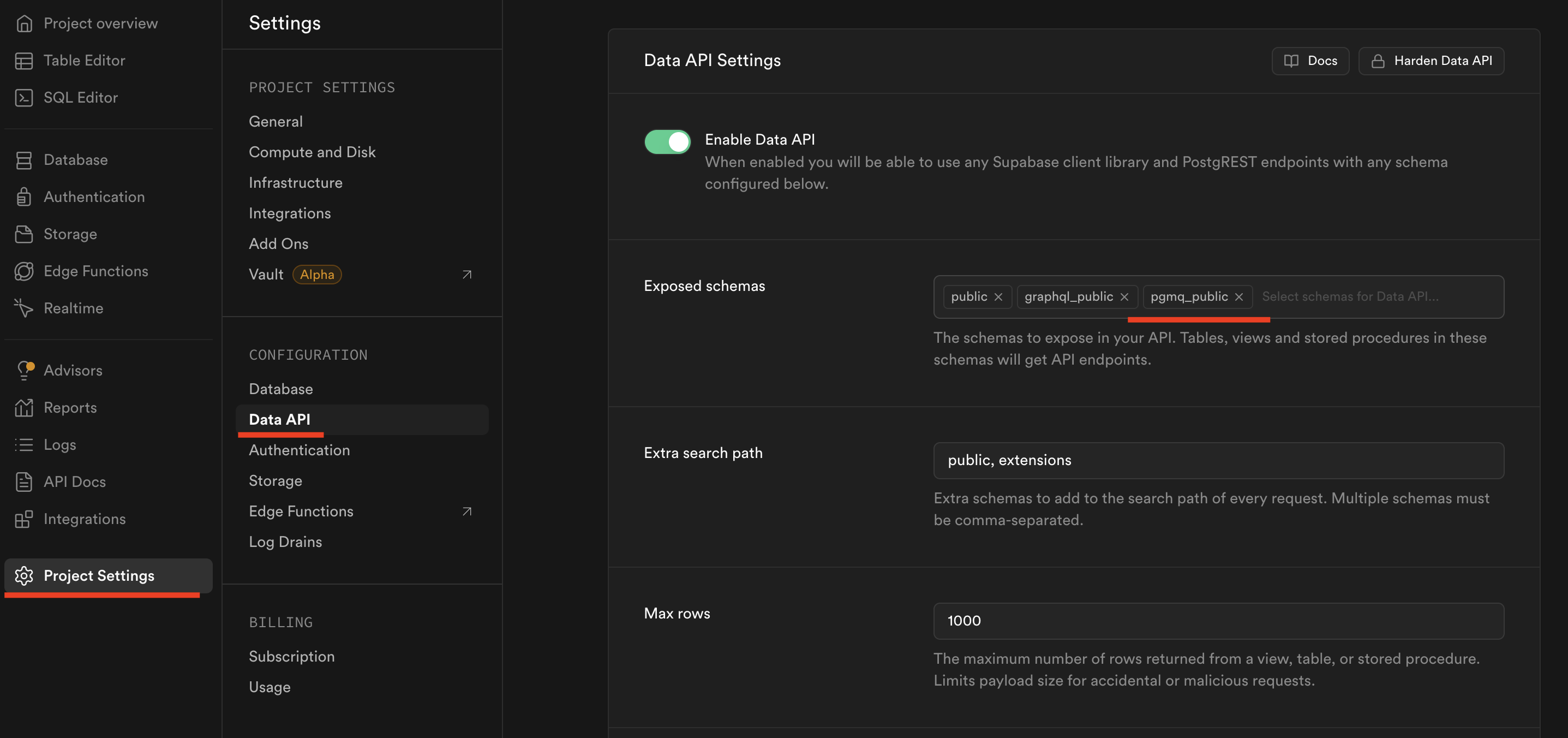
Create a database trigger that queues events for embedding generation
First we have to create a function to queue the response for embedding.
Use this SQL script to create the function:
-- Create function to queue a response for embedding
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION queue_response_embedding()
RETURNS trigger
LANGUAGE plpgsql
AS $$
BEGIN
-- Queue the response for embedding processing
PERFORM pgmq.send(
'response_embeddings', -- queue name configured in the previous step
jsonb_build_object(
'id', NEW.id, -- the id column of the response
'text', NEW.answer -- the answer column of the response
)
);
-- Set embedding to NULL to indicate it needs processing
IF TG_OP = 'UPDATE' AND OLD.answer IS DISTINCT FROM NEW.answer THEN
NEW.embedding = NULL;
END IF;
RETURN NEW;
END;
$$;Then, create 2 triggers to queue the embedding. One trigger will fire when a new row is added to the responses table, the other trigger will fire when an existing row is updated. This script can be used to create these triggers:
-- Create trigger to queue embeddings when responses are inserted or updated
DROP TRIGGER IF EXISTS queue_response_embedding_insert ON responses;
CREATE TRIGGER queue_response_embedding_insert
AFTER INSERT ON responses
FOR EACH ROW
EXECUTE FUNCTION queue_response_embedding();
DROP TRIGGER IF EXISTS queue_response_embedding_update ON responses;
CREATE TRIGGER queue_response_embedding_update
BEFORE UPDATE OF answer ON responses
FOR EACH ROW
WHEN (OLD.answer IS DISTINCT FROM NEW.answer)
EXECUTE FUNCTION queue_response_embedding();
Now, every time a new row is added to the responses table or an existing row is updated, a new embedding message will be added to the response_embeddings queue.
After inserting a value into the responses table, you will see the message in the queue in your Supabase dashboard as shown in the screenshot below:
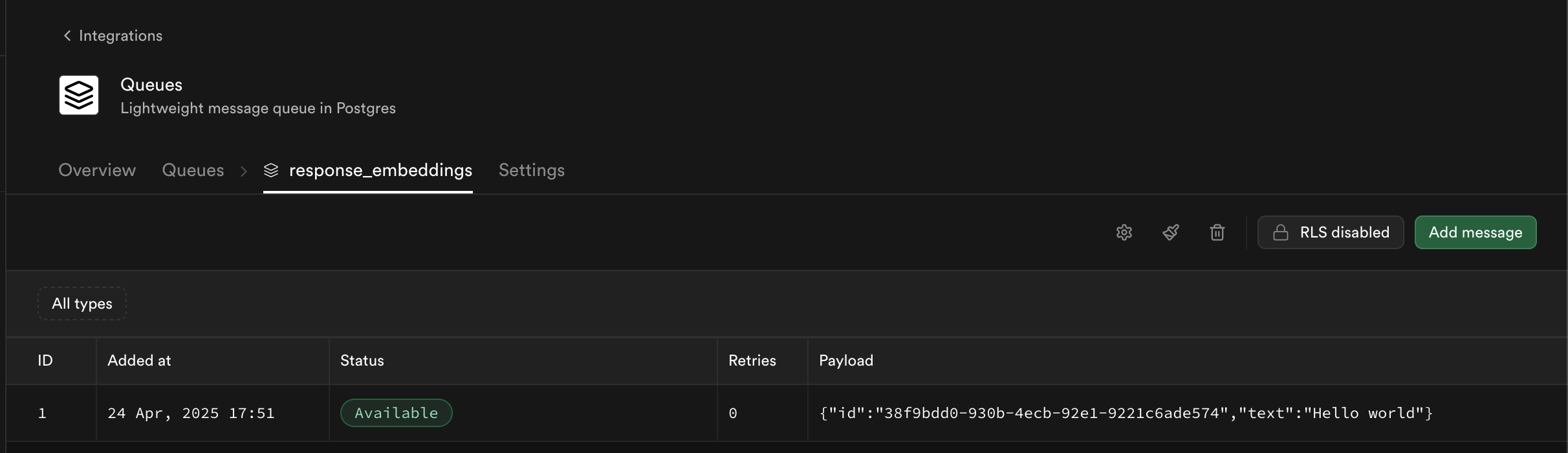
Process queue messages using a Cloudflare Worker endpoint
Create an endpoint in Cloudflare with this code (full code available in the GitHub repository):
app.post("/api/generate-embeddings", async (c) => {
console.log('Processing embeddings...')
const body = await c.req.json()
const { max_batch_size } = body
// Initialize Supabase client
const supabase = createClient(c.env.SUPABASE_URL, c.env.SUPABASE_SERVICE_ROLE_KEY)
// Read messages from the queue
const { data: queueMessages, error: queueError } = await supabase.schema('pgmq_public' as any).rpc('read', {
queue_name: 'response_embeddings',
n: max_batch_size,
sleep_seconds: 120, // 2 minutes
})
if (queueError) {
console.error('Failed to read from queue:', queueError)
throw new Error(`Failed to read from queue: ${queueError.message}`)
}
console.log(`Read ${queueMessages?.length || 0} messages from the queue`)
if (!queueMessages || queueMessages.length === 0) {
console.log('No messages found in the queue')
return c.json({
success: true,
processed: 0,
skipped: 0,
failed: [],
message: 'No messages found in the queue',
})
}
// Track message IDs that should be deleted from the queue
const processedMsgIds: number[] = []
// Process each message in parallel
await Promise.all(
queueMessages.map(async (msg: {
msg_id: number;
message: { id: string; text: string }
}) => {
// Parse the message data
const { id, text } = msg.message
console.log(`Processing embedding for form response: ${id}`)
// Generate embedding
const embedding = await generateOpenAIEmbedding(c, text)
// Update the form response with the embedding
const { error: updateError } = await supabase
.from('responses')
.update({ embedding: embedding as any })
.eq('id', id)
if (updateError) {
console.error(`Failed to update response ${id}:`, updateError)
throw new Error(`Failed to update response: ${updateError.message}`)
}
// Mark as successfully processed
processedMsgIds.push(msg.msg_id)
})
)
// Delete successfully processed messages in a single operation
if (processedMsgIds.length > 0) {
console.log(`Deleting ${processedMsgIds.length} processed messages from the queue`)
processedMsgIds.forEach(async (msgId) => {
const { error: deleteError } = await supabase
.schema('pgmq_public' as any)
.rpc('delete', {
queue_name: 'response_embeddings',
message_id: msgId,
})
if (deleteError) {
console.error('Failed to delete message:', deleteError)
}
})
}
return c.json({
success: true,
})
});This code consumes all the messages from the response_embeddings queue and generates an embedding for each message using the OpenAI API.
Schedule a CRON job to trigger the worker periodically
You can create a CRON job using the following SQL script. This creates a job that will run every 5 minutes and ping the Cloudflare worker endpoint. Replace cloudflare-worker-endpoint with the actual endpoint of your Cloudflare worker.
-- Create scheduled job to process embedding queue with the worker endpoint
SELECT cron.schedule(
'process-response-embeddings',
'*/5 * * * *', -- Run every 5 minutes
$$
SELECT net.http_post(
url := 'cloudflare-worker-endpoint', -- e.g. https://automatic-embeddings.workers.dev/generate-embeddings
body := '{"max_batch_size": 20}'::jsonb,
timeout_milliseconds := 60000
);
$$
);Assuming everything is working as expected (check the CF worker logs to double-check), you will see the embedding value in your responses table after the CRON job has run.

Troubleshooting and Next Steps
- If you encounter any configuration issues, double-check that all required Supabase extensions are enabled and configured correctly.
- Ensure the queue and the
pgmq_publicschema is exposed via the data API. - Ensure you are setting the schema correctly when doing RPC calls - e.g.
supabase.schema('pgmq_public').rpc('read') - Review your Cloudflare Worker logs for any error messages.
- For further guidance, refer to the official documentation of Supabase.
Conclusion
I hope this post has helped you understand how to automatically generate embeddings for your data using Supabase and Cloudflare Workers. If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to reach out on X or LinkedIn.
The demo app can be found here with Supabase migrations included: https://github.com/Ngineer101/automatic-embeddings